近日,标新生物与上海科技大学姜标团队、临港实验室谢成英团队合作在国际知名期刊《Cancer Research》在线发表了题为“Targeted Degradation of SOS1 Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity and Overcomes Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Tumors and BCR-ABL-Positive Leukemia”的研究论文。该研究报道了一种新型靶向SOS1(Son of sevenless homolog 1)蛋白的PROTAC降解剂SIAIS562055,通过阻断KRAS和RAC蛋白的激酶活性,发挥显著抗肿瘤作用;与KRAS抑制剂或ABL抑制剂联用时,在KRAS突变肿瘤或BCR-ABL阳性的慢性髓性白血病(chronic myeloid leukemia,CML)中展现出显著的协同增效及抗耐药作用。

KRAS是所有已知的癌基因中突变频率最高的基因之一,其突变往往与非小细胞肺癌、胰腺癌和结直肠癌等难治性癌症的发生发展密切相关。SOS1是一种鸟苷酸交换因子(guanine nucleotide exchange factor,GEF),调控RAS和RAC等小G蛋白(small GTP binding proteins,GTPases)上鸟苷三磷酸(guanosine triphosphate,GTP)和鸟苷二磷酸酸(guanosine diphosphate,GDP)的交换,进而激活下游信号通路。理论上,抑制SOS1可以有效阻断KRAS信号,从而实现对不同类型KRAS突变的广泛抑制。此外,研究表明,BCR-ABL通过招募SOS1形成复合物,驱动下游RAS、RAC等GTPases信号的激活,参与BCR-ABL驱动CML等血液肿瘤的发生发展,因此,SOS1可能是治疗CML的潜在靶点。目前尚未有SOS1抑制剂获得上市批准,多款SOS1抑制剂正在进行临床研究,旨在治疗KRAS突变肿瘤。然而,小分子SOS1抑制剂在临床研究中面临药代动力学、安全性以及单用有效性等问题,而将其作为治疗CML的潜在策略尚未得到充分探索。因此,亟需开发新的策略,以有效抑制或降解SOS1,并拓展靶向SOS1疗法的适应症。
研究团队基于SOS1小分子抑制剂BI-3406类似物、CRBN配体及多种类型连接体,合成一系列SOS1 PROTAC分子。经过分子、细胞和药代动力学研究等,筛选出对SOS1具有高降解活性的PROTAC分子SIAIS562055,该化合物能够持续降低SOS1水平并抑制下游信号,与小分子抑制剂相比,在KRAS突变型肿瘤和BCR-ABL阳性CML中均显示出更优的抗肿瘤活性。进一步的研究表明,在KRAS突变肿瘤及KRAS抑制剂获得性耐药模型中,SIAIS562055与KRAS抑制剂联合使用时表现出显著的协同抗肿瘤活性,进一步抑制ERK信号通路,诱导肿瘤退缩,并克服耐药。在BCR-ABL阳性 CML中,SIAIS562055通过上调有机阳离子载体蛋白SLC22A4,促进BCR-ABL抑制剂的主动摄取,与BCR-ABL抑制剂联用,协同增强对ABL磷酸化及下游信号的抑制,在小鼠异种移植模型和原发性CML患者样本中均表现出强大的抗肿瘤活性,且未表现明显的毒性。
综上,新型SOS1 PROTAC SIAIS562055能有效降低SOS1下游信号通路的活性,显著抑制KRAS突变及BCR-ABL阳性肿瘤体内外生长,与KRAS抑制剂或BCR-ABL抑制剂发挥协同抗肿瘤作用并克服耐药(图1)。此外,本研究拓展了SOS1靶点的适用范围,为克服KRAS及BCR-ABL抑制剂耐药问题提供了重要的实验依据。
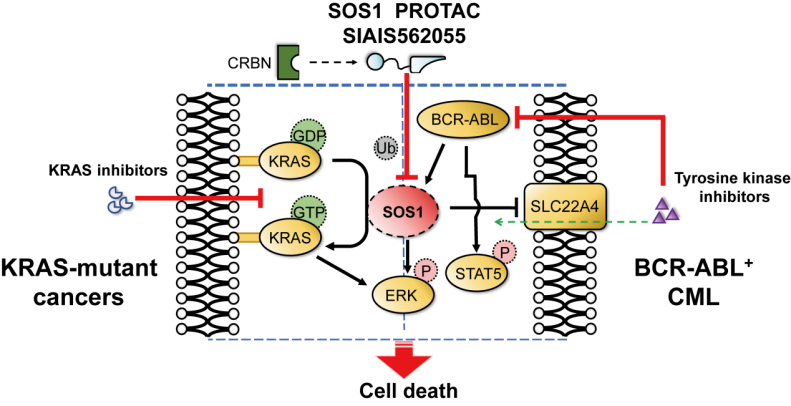
图1 SIAIS562055持续降解SOS1,抑制下游信号通路,在KRAS突变肿瘤中与KRAS抑制剂联用,以及在CML中与BCR-ABL抑制剂联用,均显示出协同增效和克服耐药作用
上海科技大学免疫化学研究所/生命科学与技术学院博士生罗自为和硕士生林宸岑为本文共同第一作者。临港实验室谢成英研究员、上海科技大学免疫化学研究所特聘教授姜标院士、标新生物杨小宝博士为本文共同通讯作者。本项目获得临港实验室(LG202101-01-06)和国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFC3401500)的资助,同时本项目还得到上海科技大学免疫化学研究所仪器平台、中国科学院上海药物研究所、上海交通大学附属第一人民医院、上海中医药大学附属曙光医院大力支持。
论文链接:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39437162/
Recently, Gluetacs collaborated with the team of Jiang Biao from ShanghaiTech University and the team of Xie Chengying from Lingang Laboratory to publish a research paper titled "Targeted Degradation of SOS1 Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity and Overcomes Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Tumors and BCR-ABL-Positive Leukemia" in the internationally renowned journal Cancer Research. The study reported a novel PROTAC degrader of the SOS1 (Son of sevenless homolog 1) protein, SIAIS562055, which significantly inhibits tumor growth by blocking the kinase activity of KRAS and RAC proteins. When used in combination with KRAS inhibitors or ABL inhibitors, it demonstrates excellent synergistic effects and overcome resistance in KRAS-mutated tumors or BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
Among all known oncogenes, KRAS is one of the genes with the highest mutation frequency, and its mutations are closely related to the development of a series of refractory cancers, such as non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colorectal cancer. SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that regulates the exchange of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and guanosine diphosphate (GDP) on small GTP-binding proteins (GTPases) such as RAS and RAC, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways. In theory, inhibiting SOS1 can effectively block KRAS signaling, thus achieving broad inhibition of different types of KRAS mutations. Moreover, studies have shown that BCR-ABL drives the activation of downstream RAS, RAC, and other GTPases signals by recruiting SOS1 to form a complex, participating in the development of blood tumors such as BCR-ABL-driven CML. Therefore, SOS1 may be a potential target for the treatment of CML. To date, no SOS1 inhibitors have been approved for marketing, and several SOS1 inhibitors are undergoing clinical studies aimed at treating KRAS-mutated tumors. However, small molecule SOS1 inhibitors face issues such as pharmacokinetics, safety, and single-use efficacy in clinical studies, and their potential as a strategy for treating CML has not been fully explored. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new strategies to effectively inhibit or degrade SOS1 and expand the indications for targeted SOS1 therapy.
The research team synthesized a series of SOS1 PROTAC molecules based on analogs of the small molecule SOS1 inhibitor BI-3406, CRBN ligands, and various types of linkers. After molecular, cellular, and pharmacokinetic studies, SIAIS562055 was selected as the most potent PROTAC, which has high degradation activity against SOS1. This compound can continuously reduce SOS1 levels and inhibit downstream signaling, showing superior antitumor activity in KRAS-mutated tumors and BCR-ABL-positive CML compared to the warhead. Further studies have shown that in KRAS-mutated tumors and acquired resistance models against KRAS inhibitors, SIAIS562055 exhibits significant synergistic antitumor activity in combination with KRAS inhibitors, further inhibiting the ERK signaling pathway, inducing tumor regression, and overcoming resistance. In BCR-ABL-positive CML, SIAIS562055 upregulates the organic cation transporter protein SLC22A4, promoting the active uptake of BCR-ABL inhibitors. When used in combination with BCR-ABL inhibitors, it synergistically enhances the inhibition of ABL phosphorylation and downstream signaling, showing strong antitumor activity in mouse xenograft models and primary CML patient samples without significant toxicity.
In summary, the novel SOS1 PROTAC SIAIS562055 can effectively reduce the activity of downstream signaling pathways of SOS1, significantly inhibit the growth of KRAS-mutated and BCR-ABL-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo, and exert synergistic antitumor effects with KRAS inhibitors or BCR-ABL inhibitors to overcome resistance. Additionally, this study expands the scope of application of SOS1 and provides important experimental evidence for overcoming resistance to KRAS and BCR-ABL inhibitors.
Ph.D. student Luo Ziwei and master student Lin Chencen from Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies of ShanghaiTech University are the co-first authors of this paper. Researcher Xie Chengying from Lingang Laboratory, Distinguished Prof. Jiang Biao from Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies of ShanghaiTech University, and Dr. Yang Xiaobao from Gluetacs are the co-corresponding authors of this paper. This project was funded by Lingang Laboratory (LG202101-01-06) and the National Key Research and Development Program (2022YFC3401500). Additionally, this project received significant support from ShanghaiTech University, the Instrument Platform of Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies at ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Affiliated Shanghai General Hospital, and Shuguang Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
关于标新生物
标新生物自成立以来受到业内的广泛关注,2022-2024连续三年获得上海市科技型中小企业称号,2023、2024连续两年入选华医榜中国生物医药科技创新价值榜最具成长性小分子创新药企业TOP10,荣获2024专精特新中小企业和创新型中小企业称号、2024年度临港新片区科创新锐企业称号、2023上海市高价值专利运营大赛百强、2023中国海归创业大赛三等奖、2023临港杯第九届创青春上海青年创新创业大赛一等奖、2022浦东新区全球高校校友科创大赛二等奖、2022中国创新制药企业TOP10、2022第十一届中国创新创业大赛成长组全国赛优秀企业奖、2022第6届医疗健康投资卓悦榜年度生物医药最佳企业、2022第五届中国创翼创业创新大赛上海选拔赛浦东赛区十佳创翼奖、2022浦东新区全球高校校友科创大赛二等奖、2022Venture50新芽榜150强、2021年度全国颠覆性技术创新大赛优秀项目、2021年第二届生物产业年度攀登榜年度最具投资潜质的新锐BioTech、2021中国生物医药产业链创新风云榜金马奖最具关注度新锐企业TOP10奖项。公司陆续获得多项科技部和上海市科委资金支持,纳入临港新片区前沿产业优秀人才安家补贴、重点产业人才补贴、人才引进重点机构名单,知识产权管理体系获得中国专利保护协会认证,多位团队核心成员陆续获得临港新片区十大科技创新先锋人物、谈家桢生命科学产业化奖、杨雄科技创业奖、东方英才创业青年领军人才、上海高层次海外人才和上海市浦江人才等称号。公司也先后成为上海科技大学创新型硕士和工程博士培养单位,并先后与十多位海内外专家教授进行科研研究合作。

注:转载请注明出处,感谢您对标新生物的关注



































 浙公网安备33011002015279
浙公网安备33011002015279 本网站未发布麻醉药品、精神药品、医疗用毒性药品、放射性药品、戒毒药品和医疗机构制剂的产品信息
本网站未发布麻醉药品、精神药品、医疗用毒性药品、放射性药品、戒毒药品和医疗机构制剂的产品信息
收藏
登录后参与评论